PSD2
What is PSD2?
The Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2 – 2015/2366/EU) is a regulation that oversees payment services and providers in the European Economic Area (EEA). It aims to boost competition, innovation, and security in the payments industry. It was built upon the original Payment Services Directive (PSD) and introduced new rules and requirements to enhance the efficiency and security of electronic payments.
Overview of PSD2
- Law: Payment Services Directive 2
- Region: European Economic Area (EEA)
- Signed Date: 08-10-2015
- Effective Date: 13-01-2018
- Industry: Payment service providers in the EEA
Personal Data Under the PSD2
Though it focuses on regulating payment services, it also affects personal data collected and processed during these transactions. Here’s a breakdown of the type of personal data typically involved under PSD2:
- Account Information: Data related to a user’s payment account, such as account number, IBAN (International Bank Account Number), and account holder name.
- Transaction Data: Details about a specific payment transaction, including amount, date, payee/payer information, and merchant details (if available).
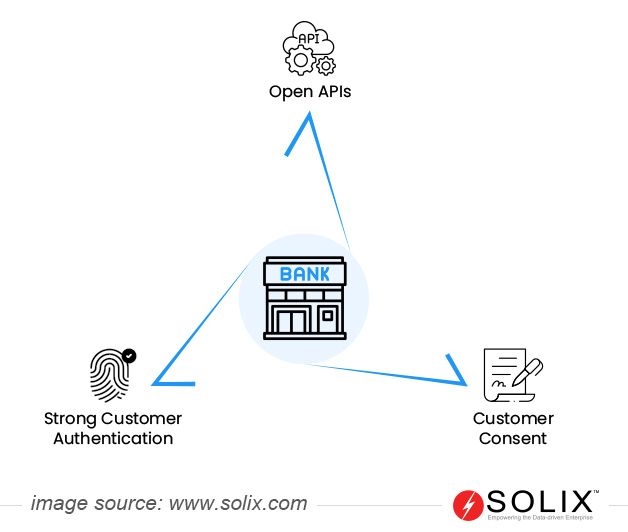
- Authentication Data: Information used for strong customer authentication (SCA) mandated by PSD2. This might include login credentials, one-time passwords, or biometric data (depending on the authentication method).
It doesn’t directly define “personal data” but relies on the existing GDPR framework. This means organizations subject to PSD2 must also comply with GDPR principles when handling personal data in the context of payment services. This ensures transparency, user control, and lawful processing of personal data.
Key Components of the PSD2
- Stronger authentication: Mandatory multi-factor authentication (MFA) for online payments increases security.
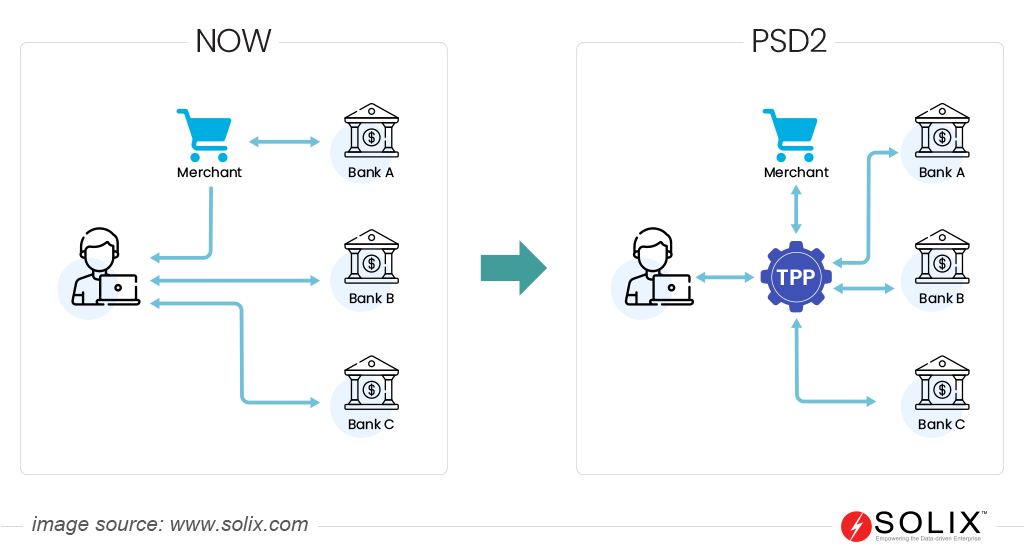
- Open banking: The PSD2 emphasizes the concept of “Open Banking.” This allows authorized third-party providers (TPPs) to access a user’s account information with explicit consent.
- Enhanced data protection: Robust data security measures and consumer control over data sharing are enforced.
Rights Under the PSD2
PSD2 aligns with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), emphasizing data minimization, purpose limitation, and user consent. Consumers can access and rectify their payment data, object to data processing and portability, and receive clear information on data usage and third-party access.
Who Needs to Comply with the PSD2?
- Payment service providers (PSPs): Banks, e-money institutions, payment initiation service providers (PISPs), and account information service providers (AISPs).
- Merchants: Accepting online payments in the EEA.
Exceptions
Micro-enterprises with very low transaction volumes have limited obligations, and specific exemptions apply to specific payment methods, such as prepaid cards with limited functionality.
Noncompliance Fines
PSD2 regulations enforce hefty penalties for non-compliance. These fines vary depending on the severity of the violation and the specific member state and can reach up to €5 million or 3% of your annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Compliance Authority
Each member state within the European Economic Area (EEA) has its designated National Competent Authority (NCA) responsible for overseeing and enforcing PSD2 compliance within its jurisdiction.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to PSD2 requirements are essential for financial service organizations. By leveraging data security solutions like data masking and other advanced security measures, businesses can mitigate compliance risks and uphold the highest data security and privacy standards. Data masking could help organizations meet regulatory requirements while preserving the utility of data for legitimate business purposes by replacing identifiable data with fictional or obscured values.
FAQs
What is PSD2, and how does it differ from PSD?
PSD2, the Second Payment Services Directive, is an updated EU regulation governing payment services. Unlike PSD, it extends beyond banks to include third-party providers (TPPs), promoting competition, innovation, and security in the payment industry.
Why was PSD2 introduced, and what are its main objectives?
The regulation aims to enhance consumer protection, foster innovation, and improve the security of electronic payments within the European Union. It seeks to create a more integrated and competitive payment market while ensuring the safety of transactions and customer data.
What are the key provisions of PSD2 regarding security and authentication?
The regulation mandates strong customer authentication (SCA) for electronic payments to enhance security. This requires at least two independent factors among knowledge (e.g., PIN), possession (e.g., card), and inherence (e.g., fingerprint) to validate transactions, reducing the risk of fraud.
What are the implications of PSD2 for third-party providers (TPPs)?
The regulation presents opportunities for TPPs. It allows them to offer innovative payment services and access customer account information through open APIs provided by banks. This enables TPPs to develop new products and services, enhancing competition and customer choice in the market.





