Data Silo
What is a Data Silo?
A data silo refers to a standalone database, system, or application that stores information independently from the rest of an organization’s data infrastructure.
These silos often arise when different departments or teams within an organization use separate tools or systems, resulting in fragmented data storage. The lack of integration between these silos makes it difficult to access and share information across the organization.
Data silos are a common challenge faced by organizations in their data management journey. These isolated repositories of information can hinder collaboration, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making.
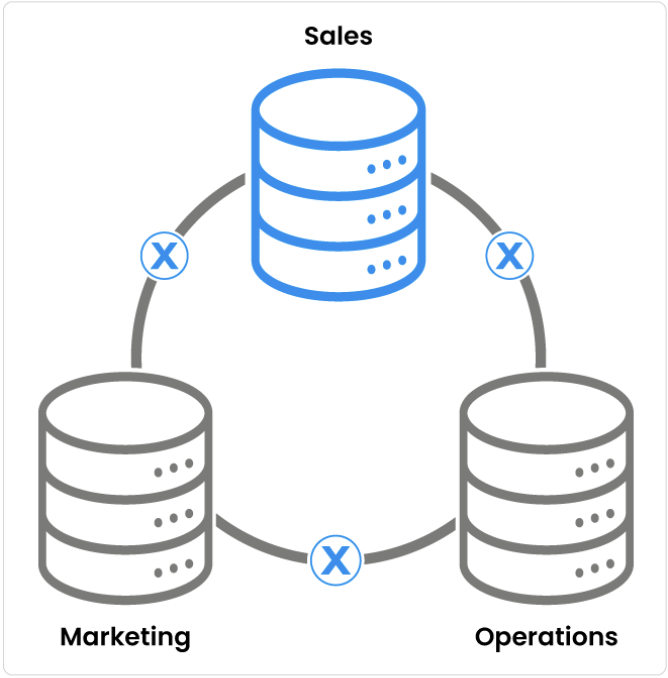
Common Causes for Data Silos
Data Silos can emerge due to several reasons:
- Departmental Focus: Departments often prioritize their own data needs and goals, leading to independent data collection and storage practices.
- Technological Differences: Legacy systems or incompatible technologies may prevent data integration.
- Data Governance Issues: Lack of standardized policies for data sharing and access control.
- Cultural Barriers: Resistance to change or lack of communication between departments can reinforce data silos.
Common Challenges Posed
- Limited Collaboration: Data silos inhibit collaboration between different departments, as teams may struggle to access and share critical information stored in isolated systems.
- Inefficient Decision-Making: Decisions based on incomplete or outdated information from data silos can lead to inefficiencies and suboptimal business outcomes.
- Increased Costs: Maintaining and managing multiple isolated databases can be expensive, both in terms of infrastructure costs and the resources required for data maintenance.
- Data Redundancy: Data silos often lead to duplication of information, resulting in data redundancy and inconsistencies across the organization.
How to Break Down Data Silos?
Organizatios can follow the following strategies to break down data Silos:
- Implement a Unified Data Platform: Utilize comprehensive data management solutions like a Data Warehouse, Data Lake, or Data Lakehouse, depending on the enterprise’s requirements, to consolidate data from various sources into a single, accessible repository.
- Establish Data Governance Policies: Define and enforce data governance policies to ensure consistent data standards, security, and compliance across the organization.
- Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between different departments by fostering a culture of shared data ownership and open communication.
- Utilize Data Integration Tools: Employ data integration tools to seamlessly connect and synchronize data across disparate systems, reducing redundancy and ensuring data consistency.
Benefits to Breaking Down Data Silos
Moving away from data Silos can have several benefits:
- Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: Breaking down data silos fosters a culture of collaboration and open communication across departments. Teams can access and share data more easily, leading to better coordination and more cohesive strategies.
- Improved Decision-Making: Unified data sources provide a holistic view of the organization, enabling more accurate and data-driven decision-making. Leaders can leverage comprehensive insights to identify trends, forecast outcomes, and make informed strategic choices.
- Operational Efficiency: Centralized data reduces redundancy and streamlines processes, leading to increased efficiency. Employees spend less time searching for information and more time on value-added activities, improving overall productivity.
- Customer Experience: With a complete view of customer interactions and histories, organizations can deliver more personalized and consistent experiences. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
- Innovation and Agility: Access to integrated data encourages innovation by providing a richer foundation for analysis and ideation. Organizations can respond more quickly to market changes and emerging opportunities, enhancing their agility and competitiveness.
- Compliance and Risk Management: A unified data framework helps ensure that all relevant data is captured and monitored for regulatory compliance. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and the associated penalties, while also enhancing data security and governance.
Data Silos represent a significant challenge in modern data management practices, requiring strategic alignment of technology, processes, and organizational culture to achieve effective data integration and utilization.
Addressing data silos is crucial for organizations aiming to harness the full potential of their data assets. By breaking down these barriers, businesses can improve operational efficiency, enhance decision-making capabilities, and foster a more agile and competitive environment.
FAQs
What’s the difference between a data silo and a data warehouse?
A data silo is an isolated pool of data, while a data warehouse is a centralized repository that stores data from various sources across an organization. Data warehouses are designed to be accessible and facilitate analysis, unlike silos which restrict access.
How can I tell if my organization has data silos?
There are some telltale signs:
Difficulty in obtaining data from other departments.
Departments using separate and incompatible data systems.
Inconsistent data leading to conflicting reports.
Repetitive data collection efforts across departments.
Are cloud-based solutions helpful in eliminating data silos?
Cloud-based data storage and analytics platforms can be a powerful tool for breaking down silos. These solutions offer centralized access to data, often with built-in features for data integration and collaboration. However, simply moving data to the cloud isn’t a guaranteed fix. Organizations still need to implement proper data governance and encourage cultural change to fully utilize cloud-based solutions for silo elimination.
How can data security be addressed when breaking down silos?
Data security is a valid concern when considering data sharing across departments. Here are some approaches to ensure security:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC): This limits access to data based on a user’s role and permissions.
- Data encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data anonymization: Consider anonymizing data for specific use cases where personally identifiable information (PII) isn’t required.
- Regular security audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and address any potential security vulnerabilities.





