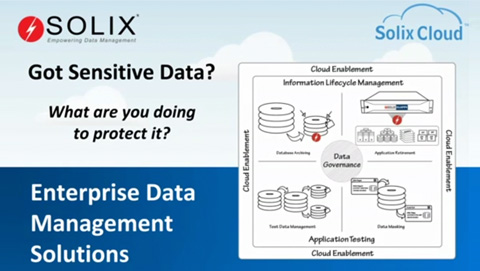
Information Lifecycle Management
What is Information Lifecycle Management?
Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) is a strategic approach to managing data from creation to disposal. It involves classifying data, optimizing storage, enforcing security measures, establishing retention policies, implementing governance, purging, and automating workflows. Organizations can reduce costs, ensure compliance, enhance security, and improve operational efficiency by efficiently managing data throughout its lifecycle.
Benefits of Information Lifecycle Management
In today’s digital age, organizations generate massive amounts of data. Effectively managing this data is crucial for several reasons:
- Cost Reduction: Not all information must be stored on expensive high-performance systems. ILM allows organizations to classify data based on its importance and move it to more cost-effective storage tiers.
- Compliance and Risk Management: ILM helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with data breaches, litigation, and non-compliance penalties.
- Improved Efficiency: It enhances operational efficiency, enabling organizations to allocate resources more effectively and focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Data Protection: By implementing security measures and access controls, ILM helps protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Business Agility: A well-implemented ILM strategy enables organizations to adapt to changing business needs and technology advancements while maintaining control over their data assets.
Key Components of ILM
- Data Classification: The first step in ILM is to classify data based on its importance, sensitivity, and regulatory requirements. Categorizing data helps prioritize resources for its management and ensure appropriate handling throughout its lifecycle.
- Storage Optimization: ILM helps organizations optimize storage resources by moving data to the most cost-effective storage tiers based on value and usage patterns. This can include on-premises storage, cloud storage, or archival solutions.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive information is a critical aspect of ILM. Organizations must implement security measures such as encryption, access controls, and data masking to safeguard data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
- Retention Policies: Establishing retention policies ensures that data is retained appropriately based on legal, regulatory, and business requirements. Retention periods depend on industry regulations, compliance standards, and internal policies.
- Data Governance: It ensures data integrity, quality, and usability by integrating data governance practices, including establishing stewardship roles, enforcing policies, and maintaining data lineage for tracking origin and usage.
- Data Lifecycle Workflows: Implementing automated workflows streamlines data management, such as migration, archiving, backup, disposal, etc., throughout its lifecycle, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
In conclusion, Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) is a holistic approach to managing data throughout its lifecycle, encompassing classification, storage optimization, security, retention policies, governance, and workflows. By implementing an effective ILM strategy, organizations can realize benefits such as cost reduction, compliance, improved efficiency, enhanced data protection, and business agility. As data grows exponentially, ILM plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to harness the value of their data assets while mitigating associated risks.
FAQ
Why is data classification important in ILM?
Data classification ensures resources are allocated based on data value and sensitivity. This allows organizations to prioritize protection efforts. It also helps them effectively comply with regulatory requirements.
What role does automation play in ILM workflows?
Automation streamlines data management tasks like migration, archiving, backup, and disposal. It reduces manual effort. Automation minimizes errors and ensures consistency in data handling processes throughout the data lifecycle.
How does ILM address security concerns related to data?
ILM uses encryption, access controls, and data masking. These protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. Protection spans the entire data lifecycle.